Table of Contents
Introduction
Mobile applications based on GPS such as Waze or Google Maps have proven to be very useful in guiding us to our destination. With such applications, it’s easy to find your way to a destination, even in an unfamiliar city. However, it is still easy to get lost indoors, where GPS satellite signals are not accurately trackable for navigation applications. For example, I’m sure that more than one of us has been lost more than once in a shopping mall or airport looking for our way to our destination and not knowing in which direction to go, it’s a frustrating situation right? Well this is the problem we are trying to solve with this proof of concept (PoC) project.
In this blogpost, I will introduce the concept of using augmented reality with the aim of creating a navigation system that can help people orient themselves and navigate within large buildings.
Context
Before beginning to explain the workings of this PoC project, let me introduce the two main concepts, which are augmented reality and Indoor Positioning Systems, to give a little context so you can better understand the overall working.
Augmented reality
One of the terms that will appear a lot in this blogpost is Augmented Reality or AR which is the foundation of this PoC. AR allows us to add layers of visual information about the real world around us using devices such as our own smartphones. This helps us to generate experiences that provide relevant knowledge about our environment, and we also receive that information in real time.
Speaking of AR what better example to give than Pokémon Go. This game has revolutionized the industry of AR-based games and has become, in a matter of days, the most popular Smartphone game in history. Another good example is IKEA Place which is an application that includes a wide variety of furniture, sofas, armchairs and stools in 3D so that we can see thanks to the AR how they would look in our house, showing the size that would occupy each product. Isn’t it amazing?


These two examples show that AR can be as much fun as it is useful. Here’s an interesting article from Forbes showing how revolutionary this technology can be in industries like education, health care, tourism and more. Also in 2017, Kevin Van den Abeele together with Michael Vandendriessche wrote a fantastic blogpost that introduces the concept of Augmented Reality in an understandable way.
Indoor Positioning System
Before explaining what Indoor Positioning Systems is, let’s first look at the types of Positioning Systems that exist today and their uses. These systems are mechanisms that allow us to detect the position of objects or events in a context or in a coordinate system.
We can differentiate between global and local:
-
Global Positioning Systems (GPS) consist of a network of satellites in geosynchronous Earth orbits that send signals that allow the receiver to calculate the distance at which these satellites are located and thus be able to calculate their position.
-
Local Positioning Systems (LPS) allow us to reach the same objective in a similar way but using local mechanisms instead of satellites (telephone towers, WiFi access points, …) and calculating the position locally.
Indoor Positioning Systems (IPS) are specific cases of LPS whose particularity is that they aim to position objects or events within a space not exposed to the open air as shown in the image below. The principles are similar in all cases, but their particularities make them different.

In this PoC we combine IPS with augmented reality without any external mechanism like sensors to determine the position, just the IPS principle. Later below I will explain how we did it.
Overview
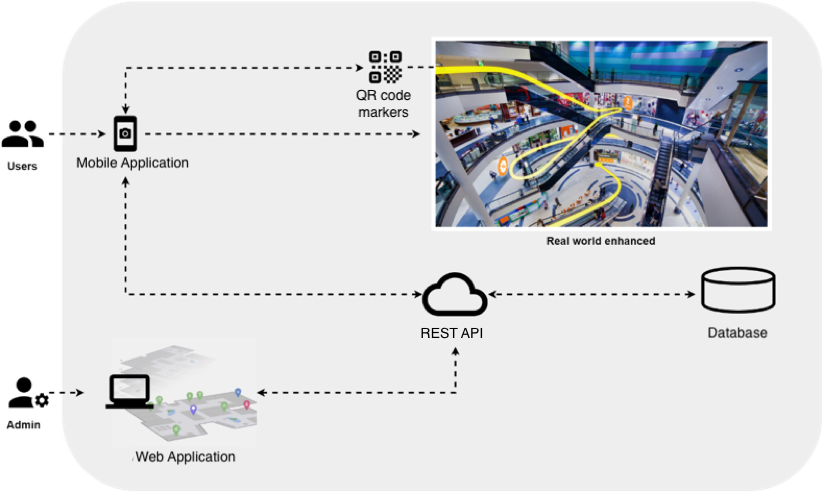
This PoC project consists of two frontend applications and a backend:
- Mobile application
- Web application
- REST API
- Database
These parts work together to accomplish the goal of helping people to navigate inside large buildings with the help of AR and they are presented below along with a brief description of the role each plays and its most important functionalities. The interaction between them will be explained later in order to understand the functioning of the system as a whole.
Mobile application
The main functionality of this application is to guide users with signals and paths drawn visually with the help of AR as you can see in the image below.
Main functionalities are:
- The ability to scan QR code markers to locate users within a building.
- Guide users to their destination with visual indications such as lines and arrows using AR.
- The possibility to search and select destinations within a building.
Used technologies
The reason for choosing React Native for the mobile application is due to its compatibility with the two major mobile platforms, Android and iOS. Another reason is its native performance as our goal was to develop an application capable of general AR natively on Android and iOS and that was thanks to the ViroReact platform. Next, the technical parts of these technologies are explained in more detail.

React Native
React Native is a multi platform framework to develop native mobile applications that is based on JavaScript and React that uses a concept similar to React’s VirtualDOM, since we also have JSX components, which will be different from HTML components and will have other tags and other names because HTML is not used.
What happens is that the React Native compiler will convert them into native interface elements for Android and iOS, which will allow these applications to have a look and feel similar to native applications, a practically equal performance and a navigation and user experience very similar to native applications, since what is being generated is native interface.

ViroReact
The technology used to create AR in this project is ViroReact which is a platform to develop augmented reality and virtual reality applications using React Native. The platform supports ARKit and ARCore for the development of AR, thus encompassing the two major augmented reality development platforms under one platform. ViroReact consists of two main components, a native 3D rendering engine and a custom React extension for AR and VR development.
Some of the advantages of ViroReact are:
- Create an application from scratch or add AR/VR features to an existing application.
- Possibility of mobile multi platform using the same code base.
- Like React Native, it allows to check the changes made only by updating the app.
- Easy to learn as it uses a markup language, which makes it quite intuitive.
- It is an open source platform, which allows you to find code that can be reused in your application.
- It is not necessary to use Xcode or Android Studio.
In 2018, Ryan De Gruyter together with Michael Vandendriessche wrote an interesting blogpost that teaches how to create augmented reality with ViroReact.
Web application
This web application is intended for administrators who are allowed to manage the system as a whole as you can see in the image below.

Main functionalities are:
- Upload a plan of a building to have a reference on which to work.
- Ability to manage destinations and routes within a building having as reference the plan of a building.
- Ability to manage and print QR code markers to be used as reference points in the physical world.
Used technologies

React
React is a library written in JavaScript, developed on Facebook to facilitate the creation of web applications in a more orderly way and with less code than if you use pure Javascript or libraries like jQuery focused on the manipulation of the DOM. It allows views to be associated with data, so if the data changes, so do the views.
React uses what is called the virtual DOM which is a representation of the DOM but in memory, which React uses to significantly increase the performance of components and frontend applications. Basically, when a view is updated, React takes care of updating the Virtual DOM, which is much faster than updating the browser’s DOM (real DOM). When React compares the Virtual DOM with the DOM of the browser, it knows exactly which parts of the page to update and saves the need to update the entire view.
REST API
The REST API is responsible for connecting the two frontend applications with the database to provide the functionalities and data necessary to carry out navigation in a building.
Used technologies
Our goal here was to develop a REST API capable of carrying CRUD operations to serve our frontend with the necessary data and functionalities such as providing points of interest to the mobile application or creating them from the web application with the help of an administrator.

NestJS
The framework used to create our backend is NestJS which is a framework based on NodeJS and TypeScript that abstracts you from the use of Express and Socket.io through decorators, has injection of dependencies “inspired” in Angular and allows to modularize our applications applying concepts of orientation to objects and functional and reactive programming.
The official documentation is another of its strong points that you can find here and there is an official repository with many didactic examples.
Database
We needed a database capable of representing real-world entities such as points of interest and their relationships in a graphical way and that’s when we came across the fantastic database Neo4j. Below are the advantages offered by this graphical database.
Used technologies

Neo4j
Neo4j uses graphs to represent data and the relationships between them. A graph is defined as any graphical representation formed by vertices (illustrated by circles) and edges (shown by intersection lines). As shown in the image below.
Databases oriented to graphs such as Neo4j perform better than relational (SQL) and non-relational (NoSQL). The key is that, although data queries increase exponentially, Neo4j’s performance does not decrease, as opposed to relational DBs such as MySQL.
How it works
Now that these applications have been introduced, we are going to look at the interaction between them in order to better understand the functioning of the system as a whole.
Let’s start from the perspective of the user who has access to the mobile application as seen in the image below.
Let’s put your favorite mall on the scene for a moment. In this mall you would find markers with QR codes strategically placed so that they are visible, and you have easy access to them. Each QR contains contextual information such as a unique identifier and the building and floor in which it is located.
Imagine you are looking for a particular shop, the first step would be to scan the marker closest to you with the mobile application. This would send the information contained in the QR to our REST API and it would take care of obtaining the necessary information from the database by querying the information obtained from the QR. This information will be sent back to the mobile application, which contains all the points of interest around you, such as shops, escalators and much more. Now it’s time for the funniest part of the process, to visualize these points of interest with AR as shown in the following video.
Are you wondering how this happens? Well this process is carried out with the ViroReact platform. First of all, we must take into account that the AR world is three-dimensional, so we have x, z and y-axis as shown in the image below.
The AR scene starts from the point where the camera is located, which is usually [x=0, y=0, z=0] and the objects are located around it with different coordinates. In this case we are going to focus only on x and z-axis because y-axis represents the height of the objects so it will be constant.
The points of interest we receive contain geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) where they are located in the real world. The AR world does not understand geographic coordinates, so we have to convert these GPS coordinates to point x, z and y-axis in meters taking as reference the initial position of the AR camera. For this we use a technique called Web Mercator projection and in this way, we have our points of interest integrated into the real world as shown in the video above.
Going back to our example before the mall, you wondered how this system would be implemented in a mall, didn’t you? Well there, the web application intended for administrators or operators who are responsible for indicating where each point of interest is located in the building comes into play. The process is shown in the following video.
Conclusion
As shopping malls, hospitals, airports, universities and other indoor spaces become more complex, the need for indoor navigation systems increases. The lack of GPS support in indoor environments has always made this a challenge. But with augmented reality, it is possible to solve this problem as demonstrated in this blogpost.
Applications that implement Augmented Reality are able to improve the user experience through their numerous current applications and the potential they offer for the future. These systems can significantly improve many areas of our lives. From navigating airports to shopping malls, AR can take us to our destination much faster than ever before.